Our technology
Renishaw's metal powder bed fusion additive manufacturing systems can build complex metal parts as a solution for a wide range of industry needs.
Metal additive manufacturing technology
Our technology can build complex shapes that are not possible with traditional casting and machining methods, or subtractive techniques. Parts can be solid, or contain hollow elements with or without lattice structures. In order to optimise parts, engineers are increasingly designing for the additive manufacturing process.
Renishaw apply metal powder bed fusion technology, as classified by ASTM International (formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials). This is the accurate term, although the technology is still often referred to as layer melting, metal additive manufacturing, metal 3D printing, laser sintering or metal AM.
Learn more about the process and how we control the quality of our finished products.
The additive manufacturing process
How does the additive manufacturing process work? Learn how below.
1. Loading powder
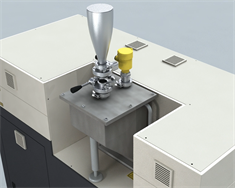
Loading metal powder before and during build.
2. Build plate loaded

Build plate is loaded into the system chamber and secured.
3. Build preparation
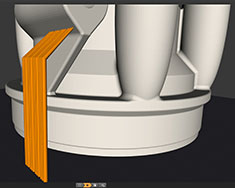
Offline build preparation file is exported to the additive manufacturing system.
4. Remove air
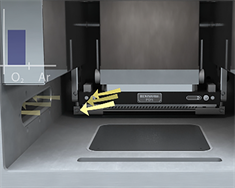
Build chamber is prepared with vacuum removal of air.
5. Inert gas
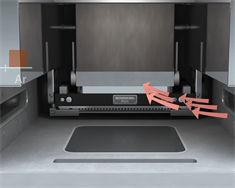
Chamber is filled with argon inert gas - class leading low gas consumption.
6. Powder delivery
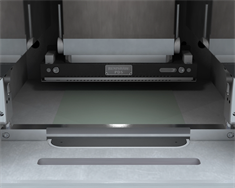
Layer of metal powder is delivered.
7. Laser melting
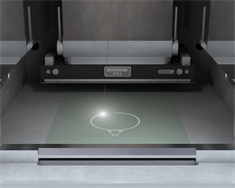
Laser melting using a fibre laser.
8. Building in layers

Build plate moves down and next layer is built up.